Urinary Tract Infection (UTI): Causes and How to Prevent It
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are among the most common health issues affecting millions of people worldwide. While UTIs can occur in anyone, they are more prevalent in women due to anatomical differences. If left untreated, UTIs can escalate into serious health problems, including kidney infections. This article will explore the causes of UTIs, their symptoms, and effective prevention methods.
What is a UTI?
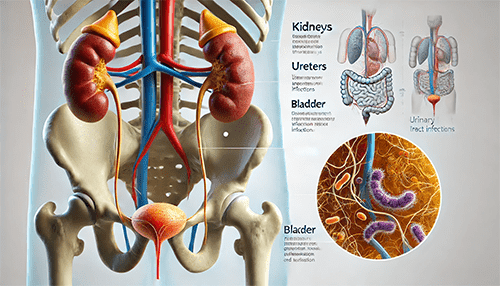
A urinary tract infection is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most infections occur in the lower urinary tract — the bladder and urethra. Bacteria are the primary cause of UTIs, though fungi and viruses can also lead to infections in rare cases.
Common Causes of UTIs
Understanding the causes of UTIs is crucial for prevention and management. Here are some of the primary factors:
Bacterial Infection
The majority of UTIs are caused by the bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli), which naturally resides in the gut. When these bacteria enter the urinary tract, they can multiply and cause infection.Poor Hygiene Practices
Improper wiping after using the bathroom can introduce bacteria from the anus to the urethra. This is especially common in women due to the close proximity of these areas.Sexual Activity
Sexual intercourse can push bacteria into the urethra, increasing the risk of infection. Women who are sexually active are particularly vulnerable to UTIs.Holding Urine for Too Long
Retaining urine in the bladder for extended periods allows bacteria to grow and increases the risk of infection.Medical Conditions
Conditions like kidney stones, diabetes, or an enlarged prostate can obstruct the urinary tract, making it easier for infections to occur.Weakened Immune System
A weakened immune system can make it harder for the body to fight off bacterial infections, increasing the risk of UTIs.Use of Certain Products
The use of spermicides, diaphragms, or harsh soaps can irritate the urethra, making it more susceptible to infection.
Symptoms of a UTI
Symptoms of a UTI can vary depending on its severity and location. Common signs include:
- A burning sensation during urination
- Frequent urge to urinate, often passing small amounts
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine
- Lower abdominal pain or discomfort
If the infection spreads to the kidneys, symptoms like fever, chills, nausea, and back pain may develop.
How to Prevent UTIs
Prevention is key when it comes to avoiding the discomfort and potential complications of UTIs. Here are some effective strategies:
Maintain Proper Hygiene
- Always wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria from spreading.
- Keep the genital area clean and dry, particularly after physical activity or swimming.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria out of the urinary tract, reducing the risk of infection. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily.Urinate Regularly
Avoid holding in urine for long periods, as this can give bacteria the chance to multiply. Always empty your bladder completely.Empty Your Bladder After Sexual Activity
Urinating after intercourse can help flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urinary tract.Avoid Irritants
Avoid using perfumed soaps, sprays, or douches in the genital area, as they can irritate the urethra and increase the risk of infection.Choose the Right Clothing
Wear loose-fitting, breathable fabrics like cotton to reduce moisture buildup, which can encourage bacterial growth.Consider Probiotics and Cranberry Products
Probiotics can help maintain healthy gut and urinary tract flora, while cranberry juice or supplements are believed to prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls.Seek Medical Advice for Recurring UTIs
If you experience frequent UTIs, consult a healthcare provider. They may recommend preventive measures such as low-dose antibiotics or lifestyle adjustments.
Conclusion
Urinary Tract Infections are a common but preventable health issue. By understanding their causes and taking proactive steps to maintain good hygiene, stay hydrated, and address risk factors, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing a UTI. If you suspect you have a UTI, it is essential to seek prompt medical treatment to prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery.
Implementing these preventive strategies not only keeps your urinary tract healthy but also promotes overall well-being. Share this article with friends and family to spread awareness about UTI prevention.

Post a Comment for "Urinary Tract Infection (UTI): Causes and How to Prevent It"